'Service Host SysMain' High CPU Usage

If you are a somewhat tech-savvy Windows users, you know that the first thing to do when you encounter performance issues is to check the Task Manager. It reveals valuable information about the way your hardware resources are being utilized, and it can quickly reveal if some process is taking up an extraordinary amount of resources. One of the Windows processes that users frequently research is ServiceHost SysMain. It seems to often consume large amounts of CPU and RAM resources, which could hinder the performance of the operating system as a whole, or of specific software suites.
Table of Contents
What is ServiceHost SysMain?
So, what should you do when you encounter the 'Service Host SysMain' High CPU Usage? The first thing to learn is what this process is responsible for. It is a legitimate service, which you might have encountered in older Windows version – Superfetch. Nowadays, it goes by the name Service Host SysMain, but its purpose has not changed. It is meant to analyze app usage and performance and then optimize the speed at which programs launch and close. It works in the background constantly, and it is turned on by default. Thankfully, it is possible to disable it – you will not encounter short-term or long-term issues by doing so. However, it is best to try out alternative fixes before opting to disable Service Host SysMain completely.
Restart the Computer
If any Windows services and features bug out, you should start the troubleshooting process by restarting your system. This will flush cached files and configuration and allow all Windows components to start fresh. Surprisingly, this may often resolve all sorts of issues, such as the 'Service Host SysMain' High CPU Usage problem.
Apply Windows Updates
As we already mentioned, Windows updates turned the Superfetch service into Service Host SysMain. This introduced some changes to the service's functionality, but its core purpose remained the same. Of course, Microsoft will continue releasing updates to enhance the functionality of various features – this is why it is important to apply all pending Windows updates immediately. This will enhance the system's performance, fix vulnerabilities, and improve your overall experience. Another issue that Windows users often research is the 'dwm.exe' Using 100% CPU problem.
Disable Service Host SysMain
If the above fixes do not work, then it might be time to turn off the service completely. This will not cause long-term or short-term issues, and you will not notice any performance issues. It will, however, prevent the 'Service Host SysMain' High CPU Usage issue from bothering you.
One way to do it is to:
- Open the Start Menu and find Services.
- Scroll down until you find the service SysMain.
- Right-click it, select Properties.Set the Startup Type to Disabled, and then press the Stop button.
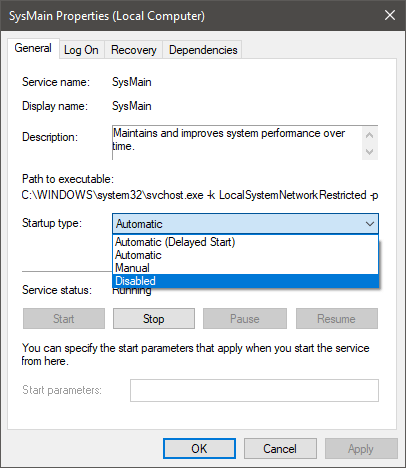
If you ever want to turn on SysMain again, you can do the same, but this time set the Startup Type to Automatic.
You can also do the same via the Windows Command Prompt. Go to Start Menu -> Command Prompt and execute the command:
sc stop “SysMain” & sc config “SysMain” start=disabled