Ransomware
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that takes control of an individual’s or organization’s computer files and networks. It does this by encrypting or locking the data and then demanding a ransom payment to unlock it, thus earning its name. This malicious software has been an increasing problem since the mid-2000s, with ransomware infections bringing companies and individuals to their knees. Today, ransomware has become a common cyber threat.
Cybercriminals typically distribute ransomware through phishing email attacks, malicious downloads, and malware-infected systems. It may also spread through security vulnerabilities in outdated software or hardware and through removable media such as USB drives.
Phishing attacks involve targeting individuals or organizations with malicious email attachments or links. When the link or attachment is opened, ransomware can be installed on the user’s computer.
Malicious downloads are files that have been maliciously altered or infected with malware and can infect a user’s computer when downloaded. Ransomware can also be installed on victims’ computers through systems already infected with malware.
In all cases, once the ransomware is installed, it will encrypt your files using strong encryption algorithms and demand a ransom payment for their return.
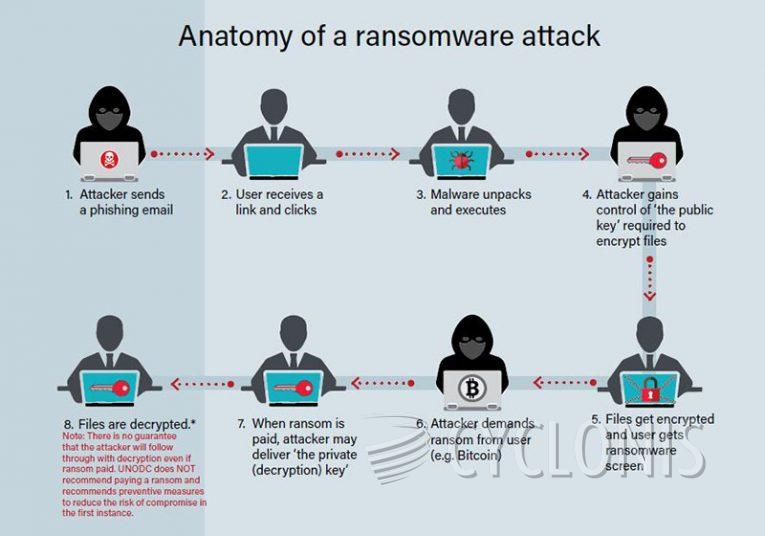
Source: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
How Ransomware Has Evolved Over the Years
Ransomware originates in the AIDS Trojan and PC Cyborg viruses of 1989. The first known modern-day ransomware attack was the “PC Cyborg” virus in 1989. The malicious code was created by a graduate student and distributed on floppy disks via Usenet. It would encrypt the system’s hard drive, preventing access to files until a monetary payment was made.
While these early ransomware attacks were not as sophisticated as those seen today, they were still effective in extorting victims. Since then, we’ve seen various iterations of ransomware become more and more malicious and difficult to detect with traditional antivirus solutions.
In the mid-2000s, ransomware began to appear as a form of “malware as a service” (MaaS). MaaS allowed malicious actors to purchase access to an online platform where they could construct and distribute their own custom ransomware. This led to the development of more complex forms of ransomware like CryptoLocker, which was responsible for over $3 million in losses.
Today, ransomware is used by threat actors to target individuals, businesses, and even government organizations. Cybercriminals will use various methods, such as social engineering or exploit kits, to gain access to sensitive systems or data. Once they have gained access, they are able to deploy their malware, which then encrypts all of the data on the system, rendering it inaccessible. As a result, victims are typically displayed a ransom note that urges them to pay a ransom in return for access to their data.
In response to this growing threat, governments and organizations have been working to develop better solutions for detecting and defending against ransomware attacks. However, due to its constantly shifting nature, ransomware remains a major threat to organizations of all sizes.
What You Need to Know: Prominent Types of Ransomware Attacks
Notable examples of ransomware attacks include WannaCry (2017), Petya/NotPetya (2017), TeslaCrypt (2015–2016), and CryptoWall (2014–2016). In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware spread quickly worldwide and affected over 200,000 computers in 150 countries. In 2016, CryptoWall infected more than 625,000 systems in the US alone. Petya/NotPetya, another ransomware attack that occurred in 2017, affected many major international companies, including FedEx and Maersk.
In addition to disrupting normal operations, ransomware attacks often cause financial losses. TeslaCrypt, for example, was estimated to have caused a total of $1 billion in damages by encrypting the data within victims’ computers and demanding payment of Bitcoins in exchange for decryption keys. CryptoWall also caused significant financial losses — it is estimated that more than $1 billion was lost in the attack.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, by 2021, ransomware damages had cost businesses around $20 billion annually. The increase in damage costs is attributed to the growing ransomware sophistication and its ability to penetrate any system regardless of geography or sector. Additionally, according to a report by Kaspersky Lab, more than 57.4 million users have been attacked with ransomware since the start of 2017.
Additionally, in 2021, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack became one of the most prominent examples of ransomware attacks to date. The attack began in late April and resulted in the disruption of fuel supplies all across the Eastern United States. Over 5,500 miles of pipeline were affected, leading to major shortages and price hikes at gas stations. The attacker responsible for the attack, DarkSide, is a Russian-based group that has been linked to numerous other ransomware attacks.
The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack has had a significant financial impact. It is estimated that the total costs associated with the attack could reach $3 billion. This includes losses from the pipeline shutdown, disruption to businesses, and costs associated with restoring systems to their former state. Some experts also speculate that these costs could be much greater and exceed $5 billion.

Source: World Economic Forum
How to Protect Yourself from Ransomware
Ransomware attacks have become common due to a number of factors, including the proliferation of ransomware-as-a-service offerings on darknet markets, the increasing use of cryptocurrency payments, and the ability to launch sophisticated campaigns involving multiple malware strains.
The most common ransomware targets are businesses and individuals who are not very good at computer security. Businesses that do not update their software and hardware do not employ antivirus software, open suspicious links or attachments, download files from untrusted websites, or use insecure networks are more likely to be targeted by this type of malware attack.
The best way to protect yourself from ransomware is to increase your overall security posture through a combination of education, prevention, and response strategies. Education should focus on teaching users how to recognize the signs of a ransomware attack and what to do if they suspect they have been targeted. Prevention is key in stopping ransomware attacks and includes:
- Using up-to-date software.
- Enabling two-factor authentication when possible.
- Creating copies of backup files regularly.
- Practicing good cyber hygiene.
- Remaining vigilant and aware of common ransomware attack vectors.
- NOT PAYING the ransom demanded by cybercriminals.
- Seeking a security expert assistance if infected.
In other words, responding to a ransomware attack quickly and effectively is essential in minimizing damage and recovering stolen data.
By following these guidelines, individuals and organizations can help protect themselves against the damaging effects of ransomware attacks. With proper education and prevention strategies, users can significantly reduce their risk of becoming ransomware victims.


















